Pricella® Primary Vascular-derived Cell Isolation and Culture Kits—Precise Isolation Empowering Vascular Research
Jul 29,2025
Isolating and culturing primary cells is a cornerstone of life science research, offering a more accurate representation of the physiological state of cells in vivo. To help researchers overcome the technical challenges of primary cell isolation, Pricella® has developed a series of high-efficiency, easy-to-use isolation kits covering six major tissue types: brain, vascular tissue, liver, cartilage, bone marrow, and heart. These kits are designed to deliver high-purity, high-viability cells quickly and consistently. In this edition of Cell Culture Academy, we spotlight the Primary Vascular-derived Cell Isolation and Culture Kits—detailing their key features, typical applications, and practical tips.
Ⅰ. Primary Vascular-derived Cell Types and Their Research Applications
Endothelial cells line the inner surface of blood vessels, forming a continuous, single-cell monolayer that acts as a barrier. They play a vital role in the exchange of substances and the regulation of vascular permeability. In addition, they are involved in key physiological processes such as the regulation of vascular tone, blood coagulation, inflammatory responses, and angiogenesis. As a result, endothelial cells are widely used in studies related to thrombosis, atherosclerosis, inflammation, and tumor angiogenesis.
Smooth muscle cells are located in the middle layer beneath the endothelium. Their primary function is to regulate the diameter of the vascular lumen through contraction and relaxation, thereby controlling blood pressure and blood flow distribution. Smooth muscle cells are commonly used in research on diseases such as hypertension, atherosclerosis, aneurysms, bronchial asthma, and pulmonary hypertension.
Ⅱ. Pricella® Primary Vascular-derived Cell Isolation Kits
1. Product Catalog
| Product Name | Cat. No. | Size |
|---|---|---|
| Rat Aortic Endothelial Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-606 | 3 Tests/10 Tests |
| Rat Aortic Smooth Muscle Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-607 | |
| Rat Pulmonary Great Artery Endothelial Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-608 | |
| Rat Pulmonary Aorta Smooth Muscle Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-609 | |
| Rat Saphenous Vein Smooth Muscle Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-610 | |
| Rat Brain Artery Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells Isolation and Culture Kit | P-CA-611 |
2. Kit Components and Brief Description of Their Functions
- Washing Solution: Used for rinsing vascular tissues while effectively preserving tissue and cell viability. It also helps minimize the risk of contamination.
- Endothelial Cell Digestive Solution (Aorta/Pulmonary Artery): Specifically formulated to digest the intimal layer of vascular tissues, efficiently breaking down tissue structure to yield an endothelial cell suspension.
- Smooth Muscle Cell Digestive Solution: Used to digest and dissociate the vascular smooth muscle layer, enabling thorough tissue breakdown and the preparation of a single-cell suspension.
- Basic Culture Medium and Supplement: Provide essential nutrients to support cell growth and promote the preferential expansion of target cell types.
- Plating Solution: Enhances cell adhesion and supports proliferation efficiency during the initial culture stage.
- Cell Filter: Removes undigested tissue fragments and debris through physical filtration, improving the purity of the resulting cell suspension.
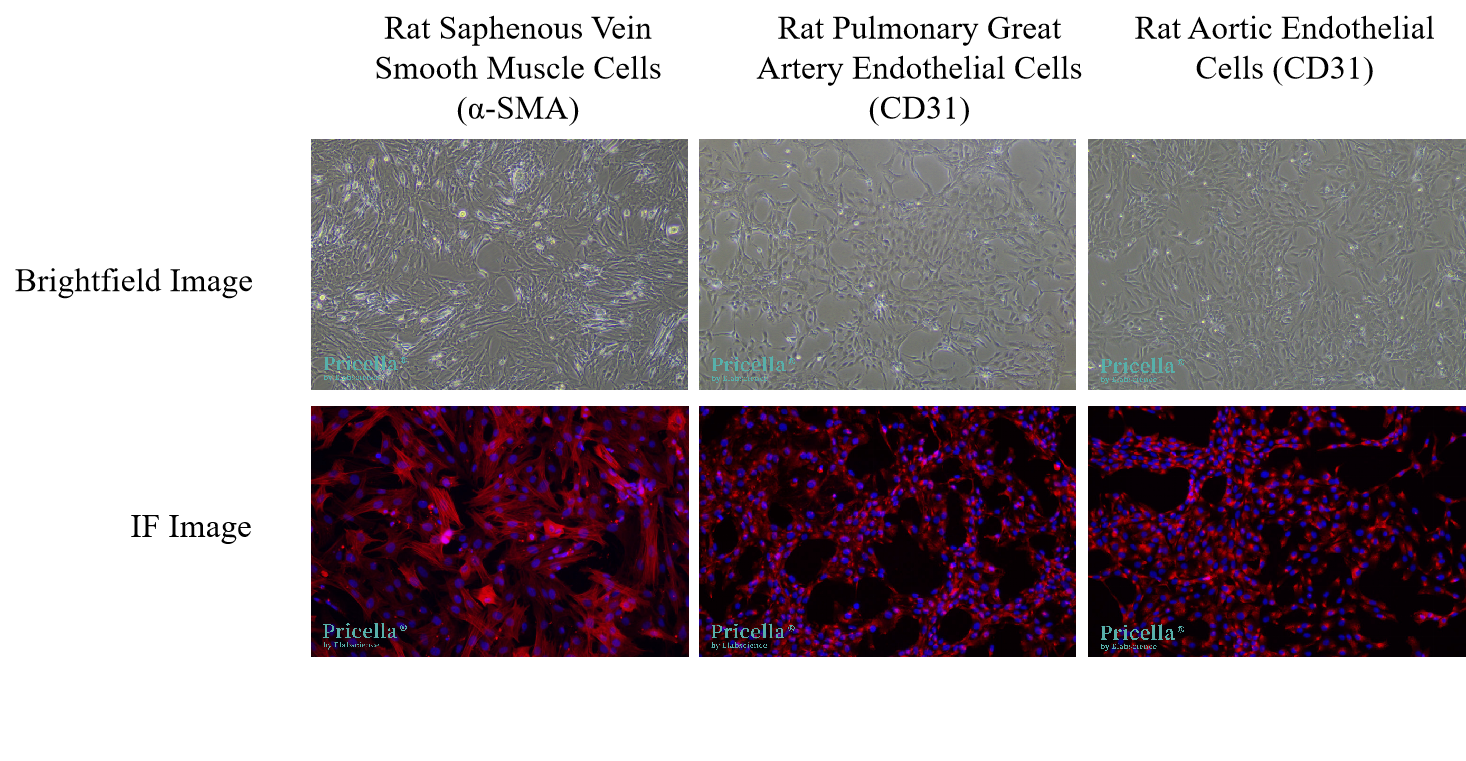
3. Cell Images from Kit Isolation
Ⅲ . Common Issues in Primary Vascular-derived Cell Isolation and Culture
1. Low Cell Purity
- To maximize cell purity, thoroughly remove any fat and connective tissue from the surface of the blood vessels.
- When isolating smooth muscle cells, carefully strip away both the adventitia and intimal layers as completely as possible.
- For endothelial cell isolation, closely control both the digestion time and the size of tissue fragments (refer to the recommended specifications in the manual). Over-digestion can lead to contamination with non-target cells and reduced purity.
2. Low Cell Yield or Viability
- Low cell yield is often the result of insufficient tissue digestion. Ensure that the digestive solution is prepared and stored according to the instructions, and monitor digestion time closely.
- Low viability is typically caused by over-digestion. To minimize cell damage, handle tissues gently during pipetting and terminate the digestion process promptly.
- During tissue collection, work efficiently, process the tissue immediately after harvesting, and keep it at low temperatures to preserve cell viability.
3. Subculturing Endothelial Cells: Key Guidelines
- Endothelial cells are relatively fragile, with limited passaging capacity and a slow proliferation rate. It is normal for these cells to exhibit delayed attachment within the first 72 h of culture. If attachment is poor, centrifuge the cells, replace the culture medium, and return them to the original dish.
- Subculture the cells once they reach over 80% confluence, using a 1:2 split ratio. Accutase is the preferred detachment reagent; if unavailable, 0.25% trypsin-EDTA may be used. In either case, strictly control digestion time to avoid damaging the cells.
Prev: From Challenges to Breakthroughs in Culturing Neurons
Next: Drug-resistant Cell Lines一Crack the Survival Code of Cancer Cells and Overcome Treatment Barriers

